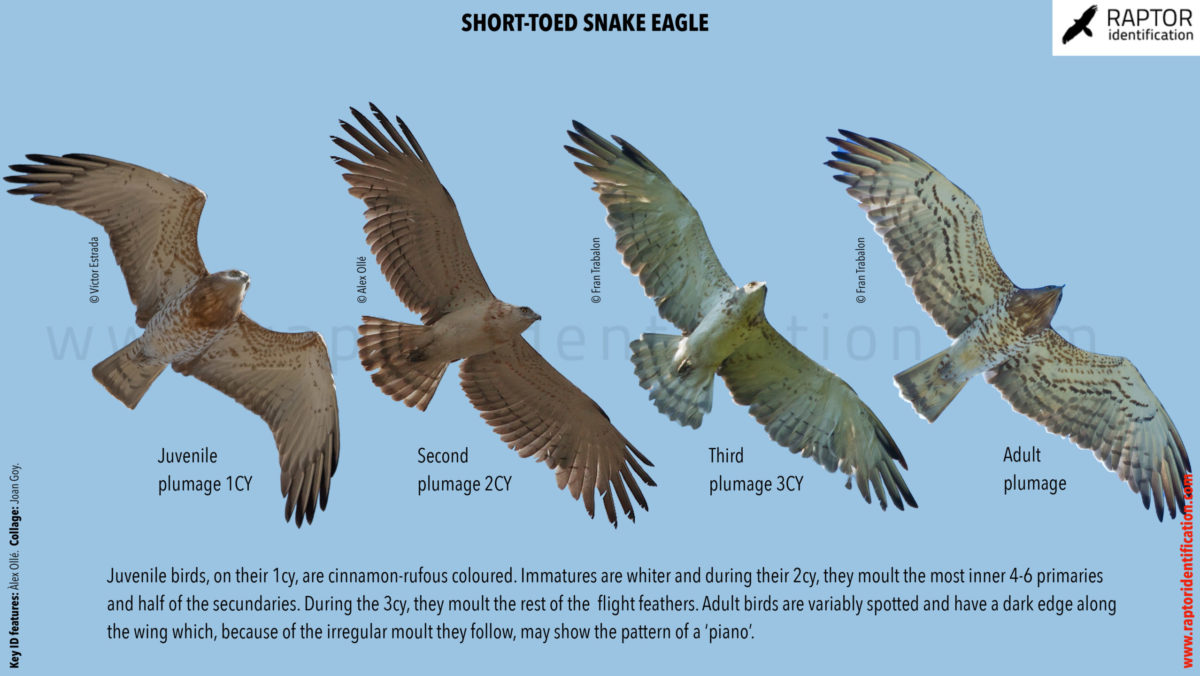
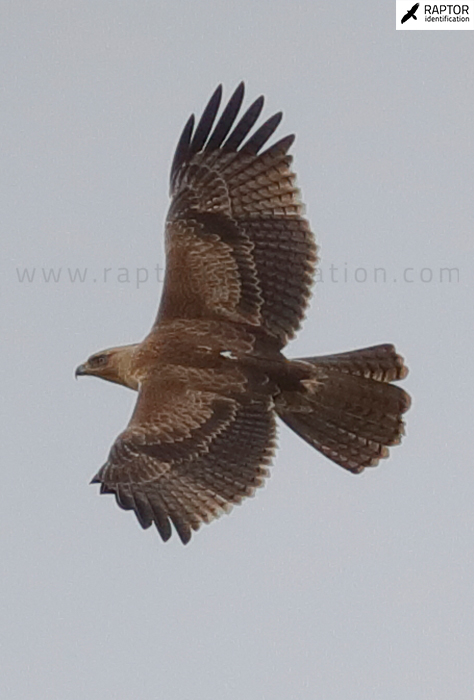
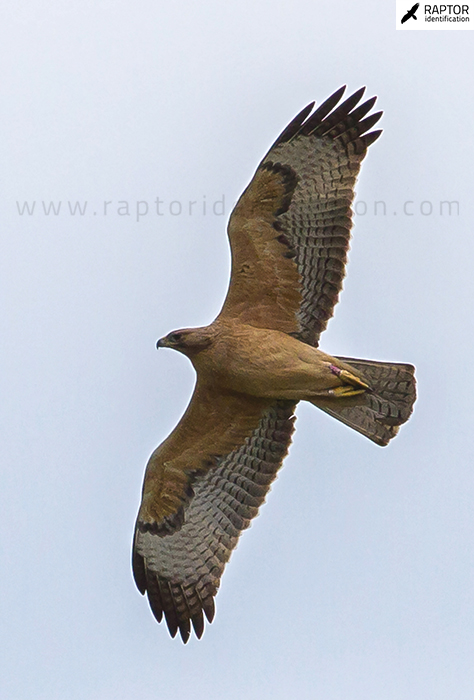
Taxonomy:
Monotypic
Status: scarce but present over a vast area, from East Europe to North China. Most of the population winters in the middle east, Africa and southern Asia. About 15% (300-400 ind.) of the European population winters in southern Europe, especially in Greece and locally in Spain, France, Italy, Albania, Bulgaria and Turkey. Very faithful to their wintering grounds.
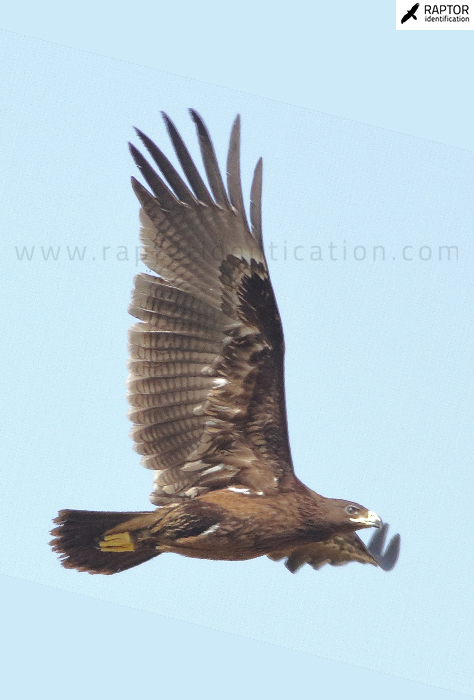
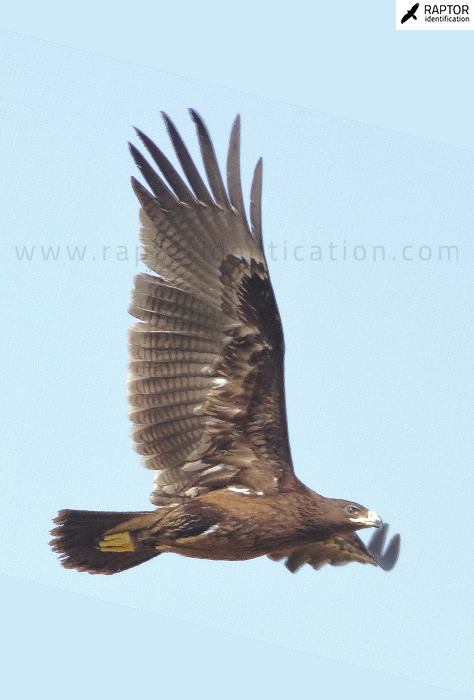
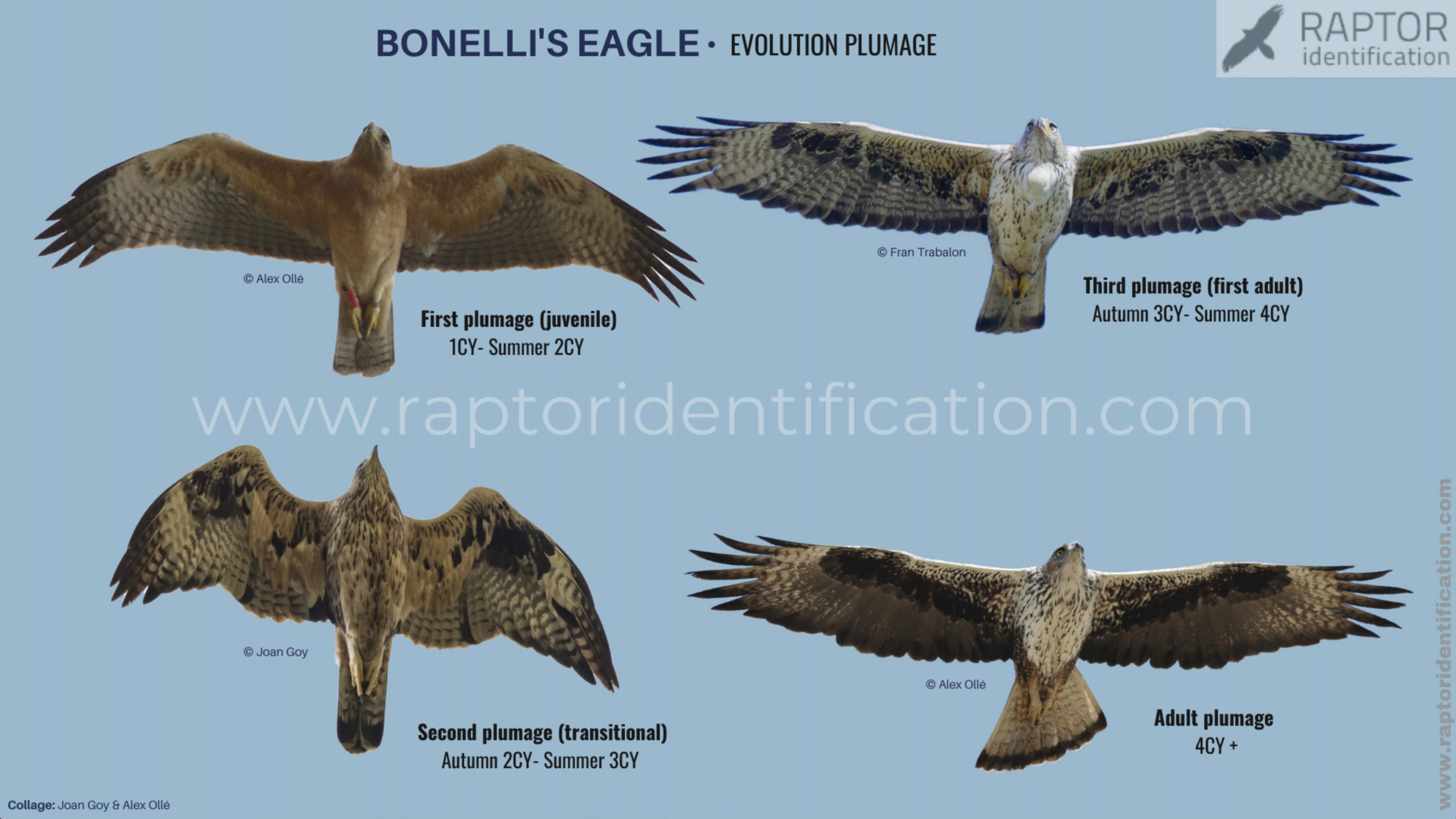
Moult: usually, immature birds only replace some of the flight feathers (rectrices and remiges) on their wintering grounds, while adults have a more extensive moult.
Second plumage: during spring and autumn, 2cy birds moult half of their innermost primaries as well as some secondaries and rectrices.
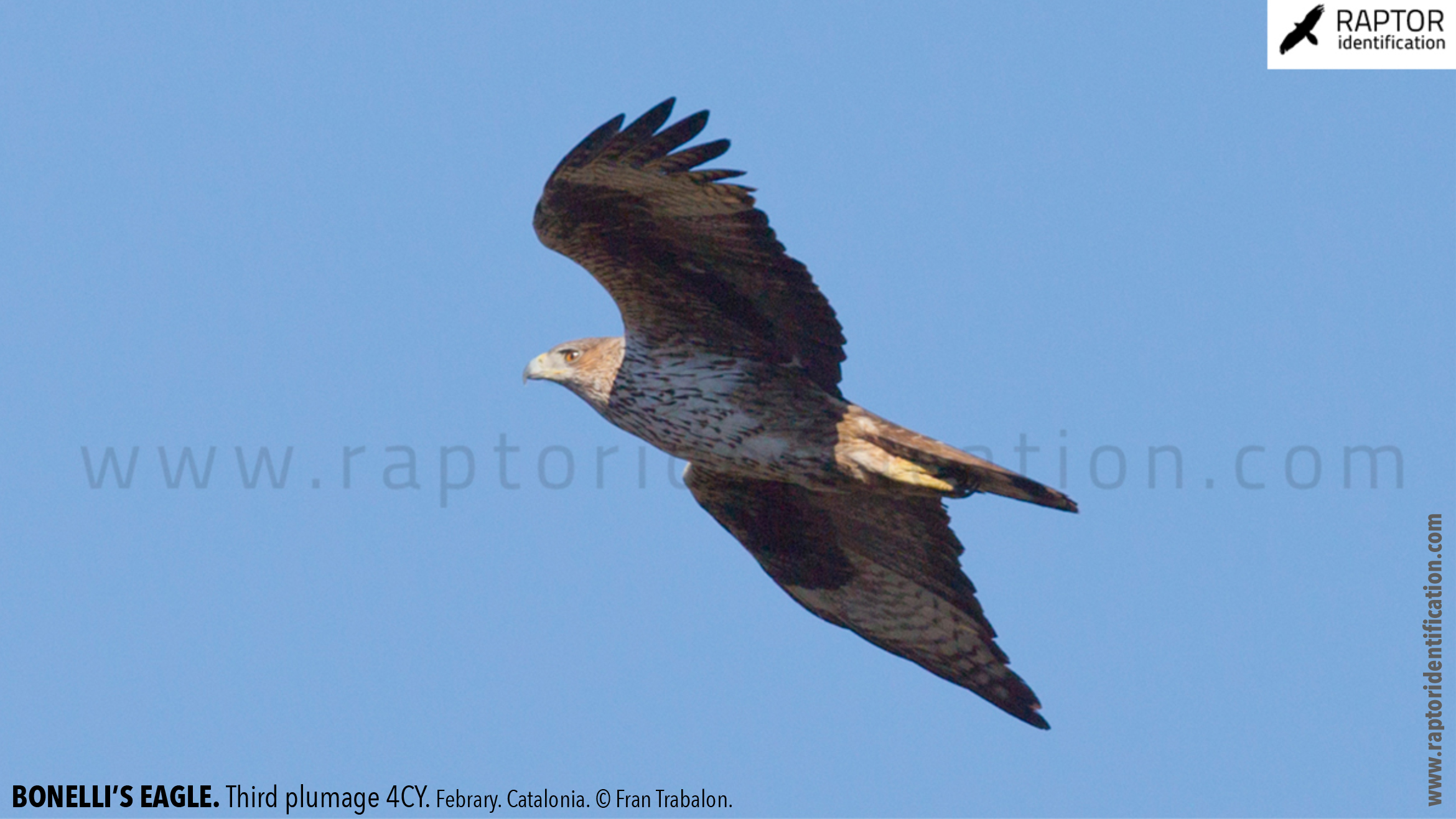
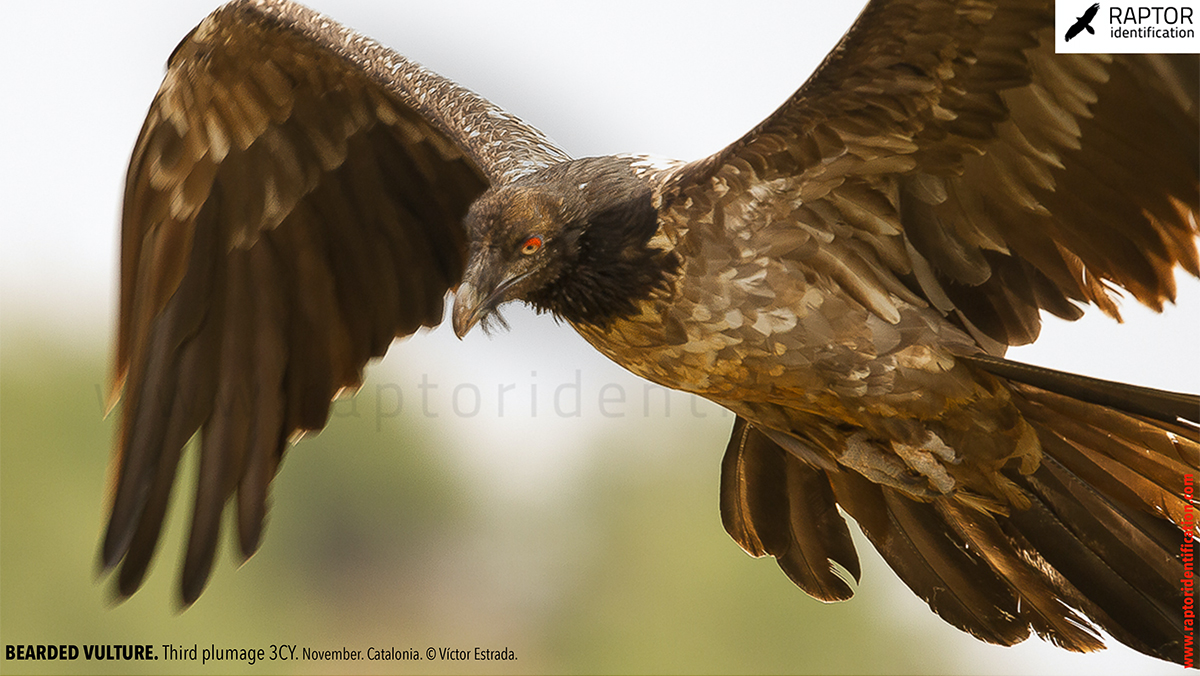
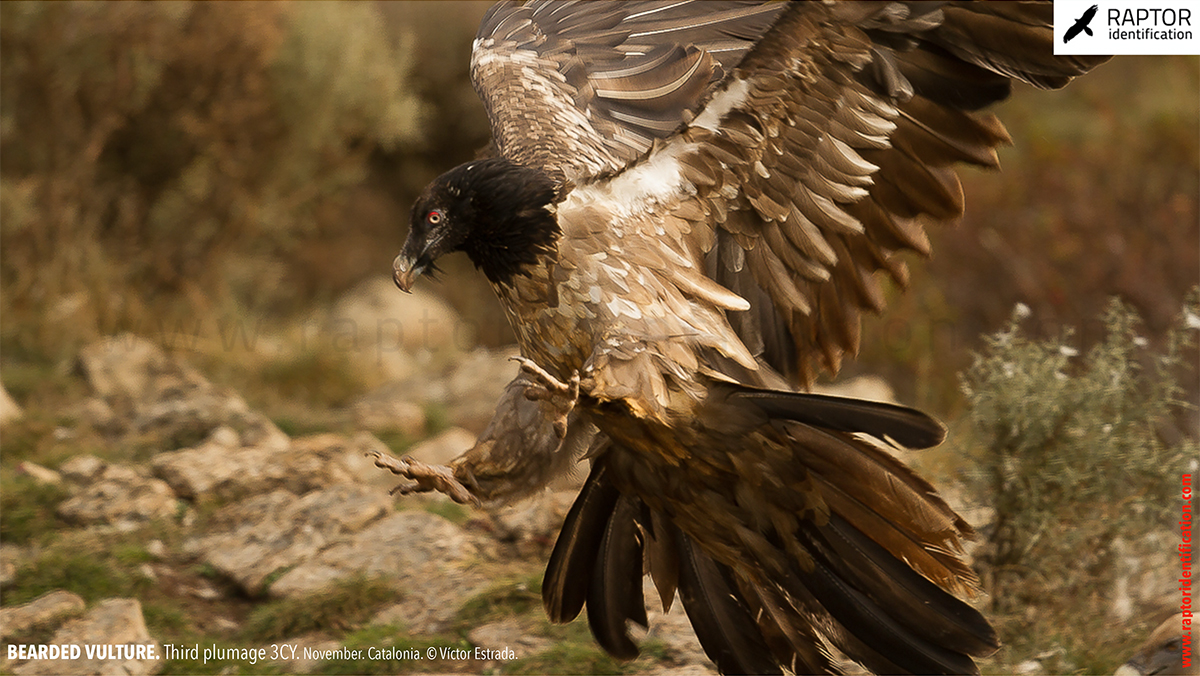
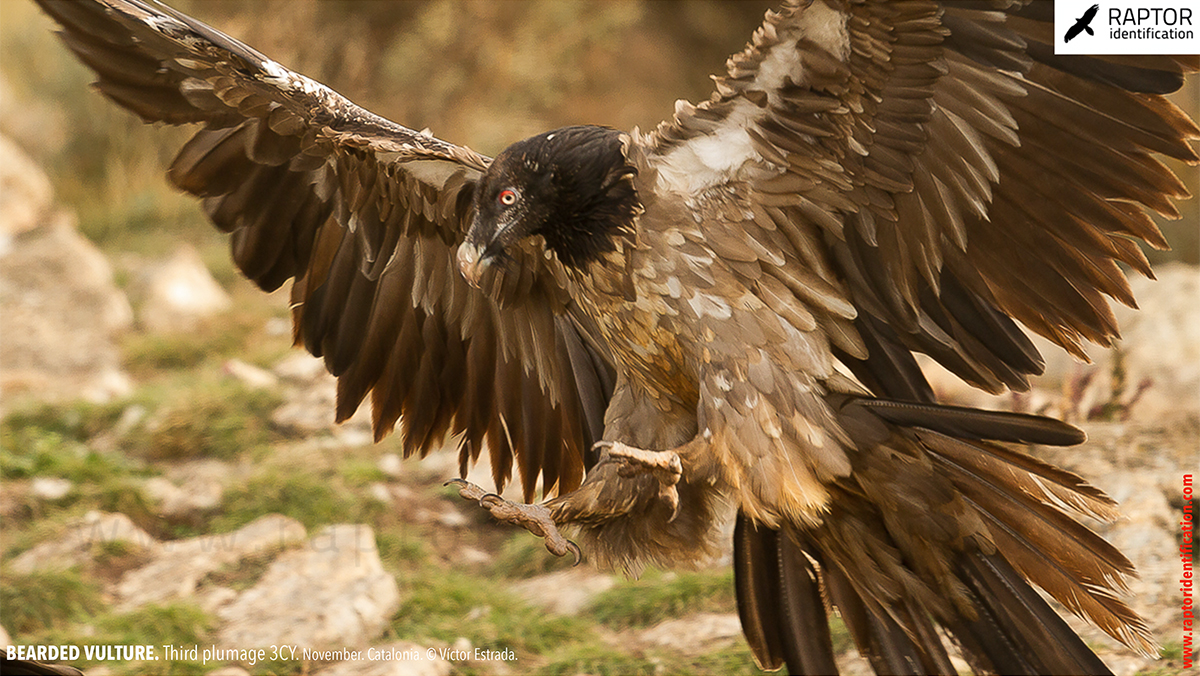
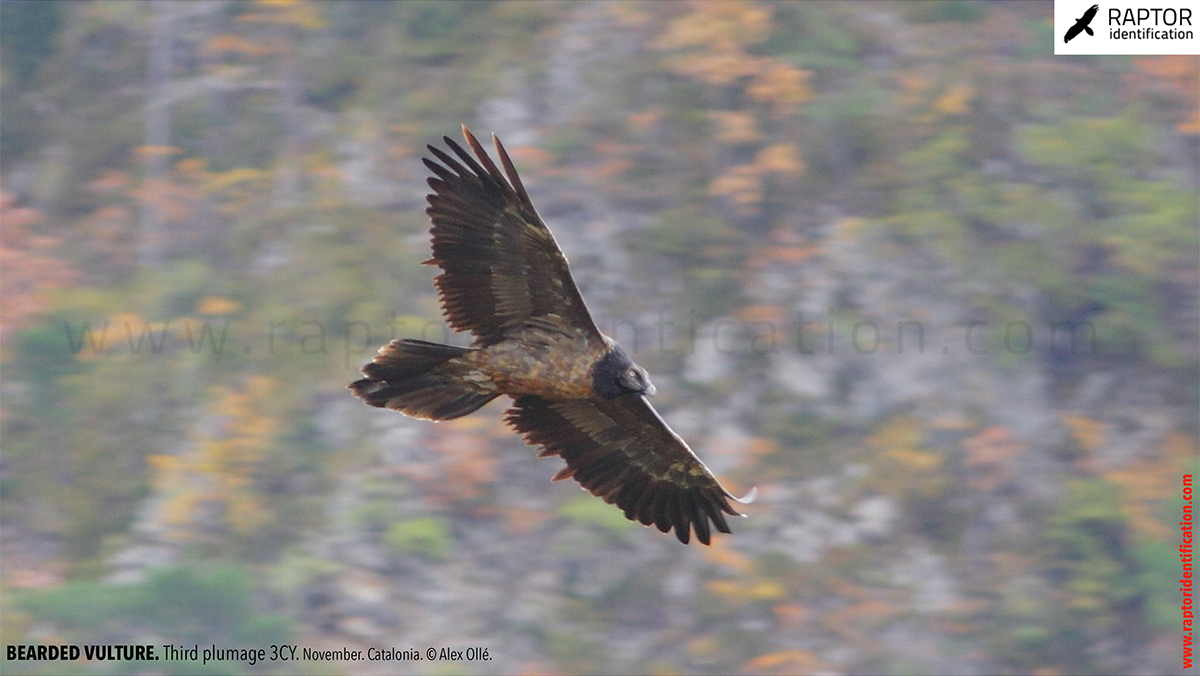
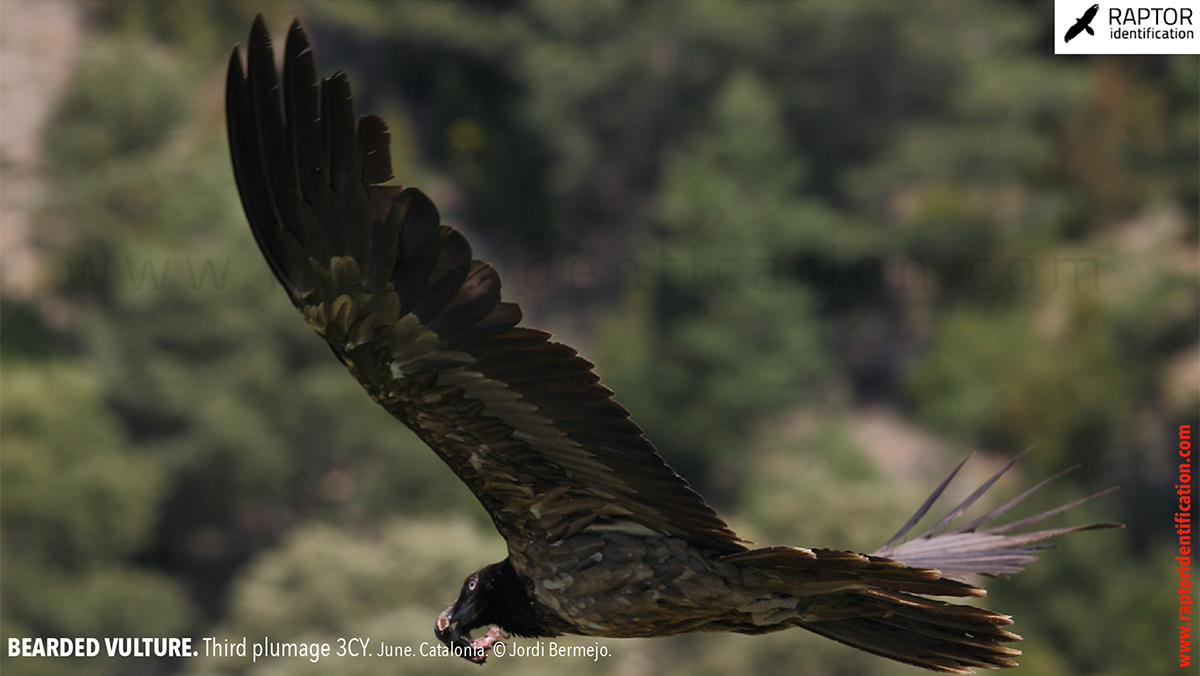
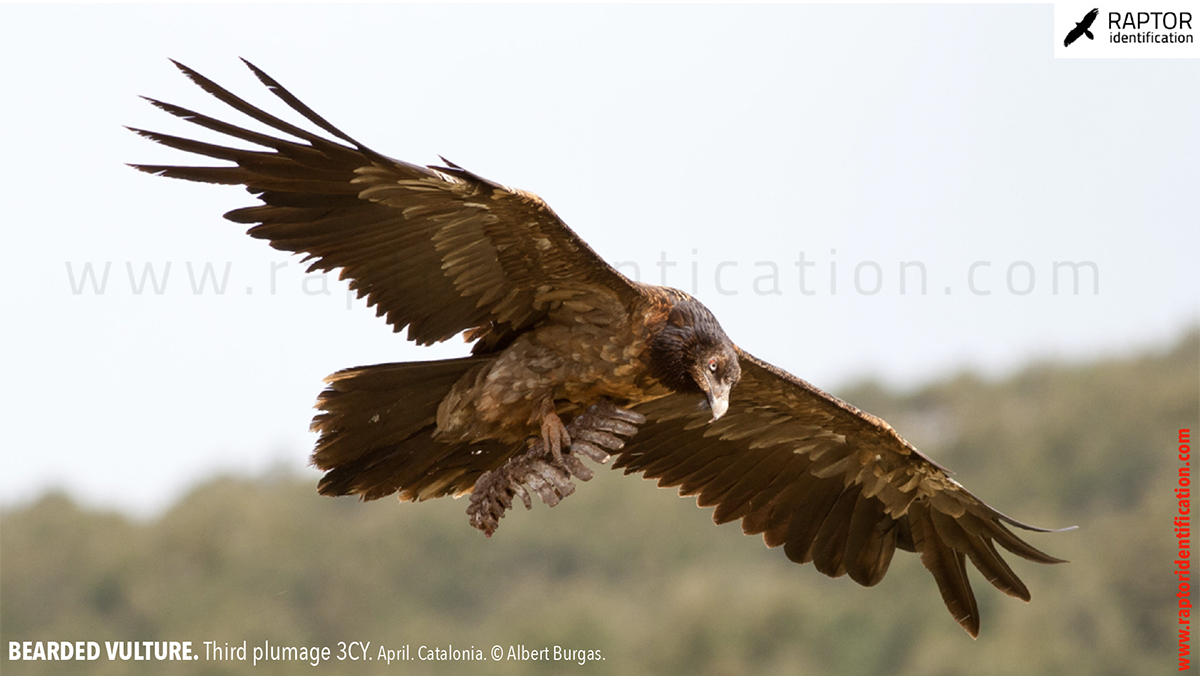
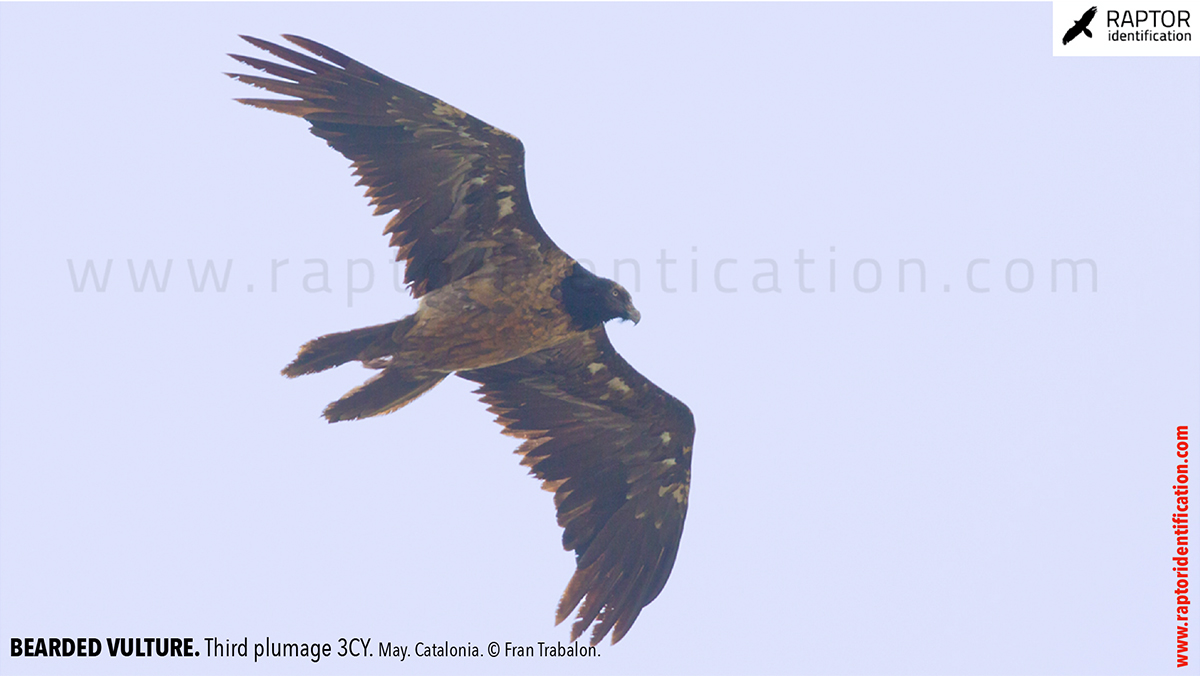
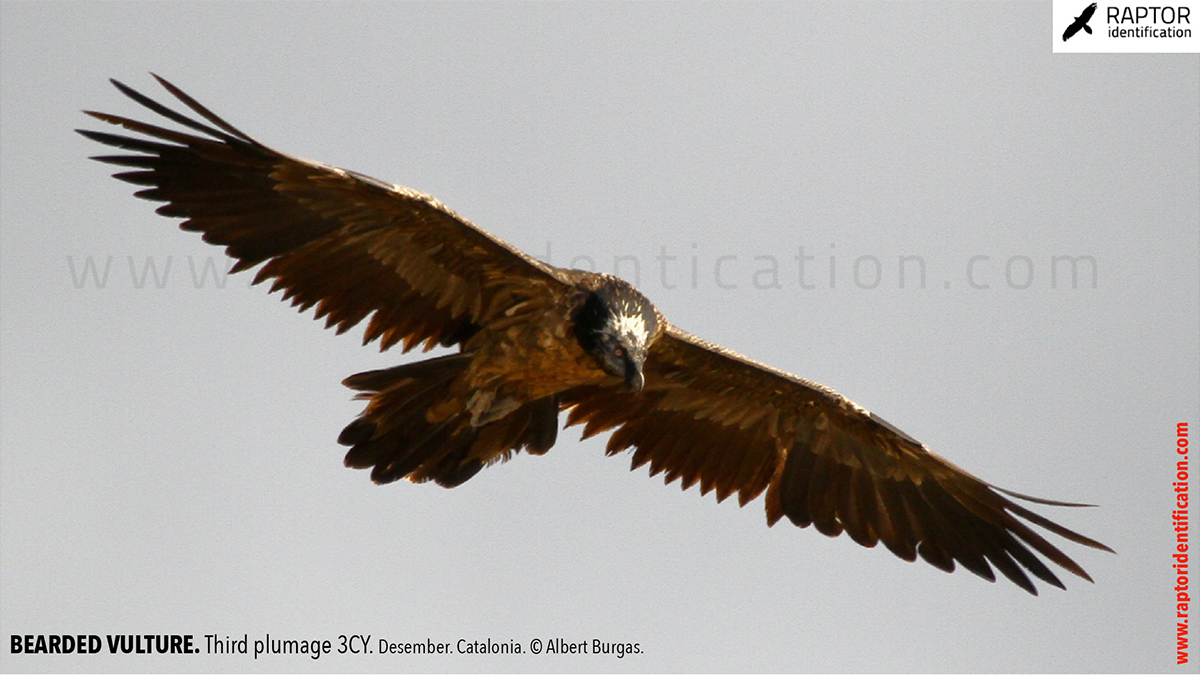
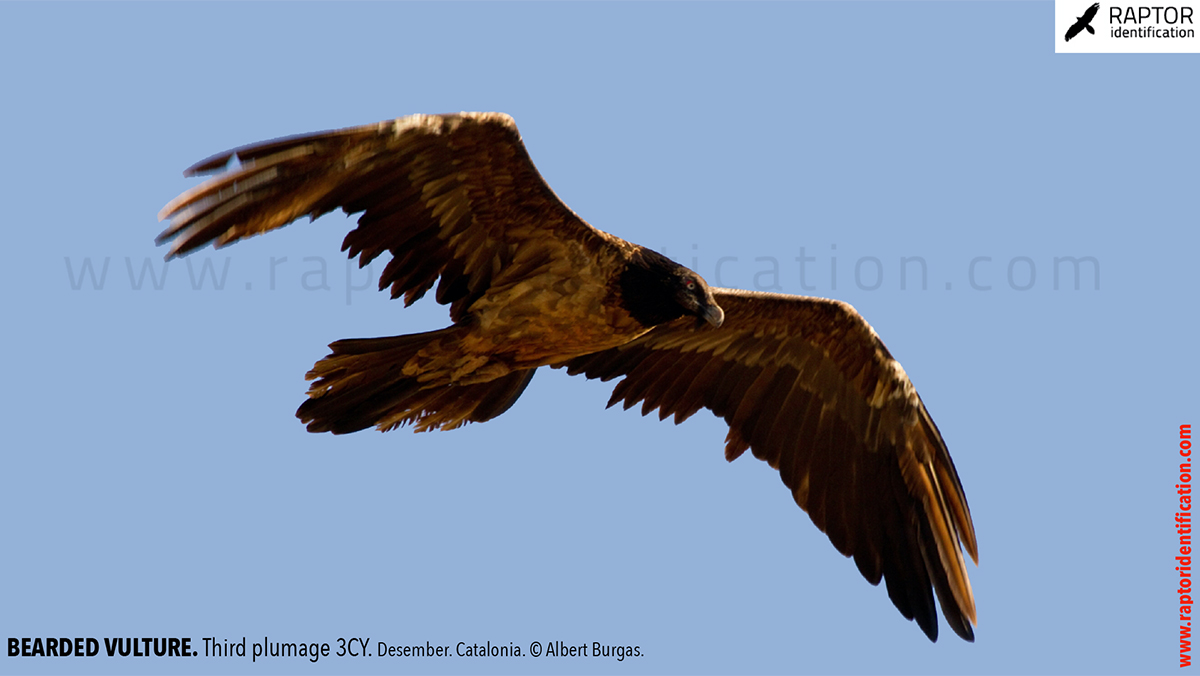
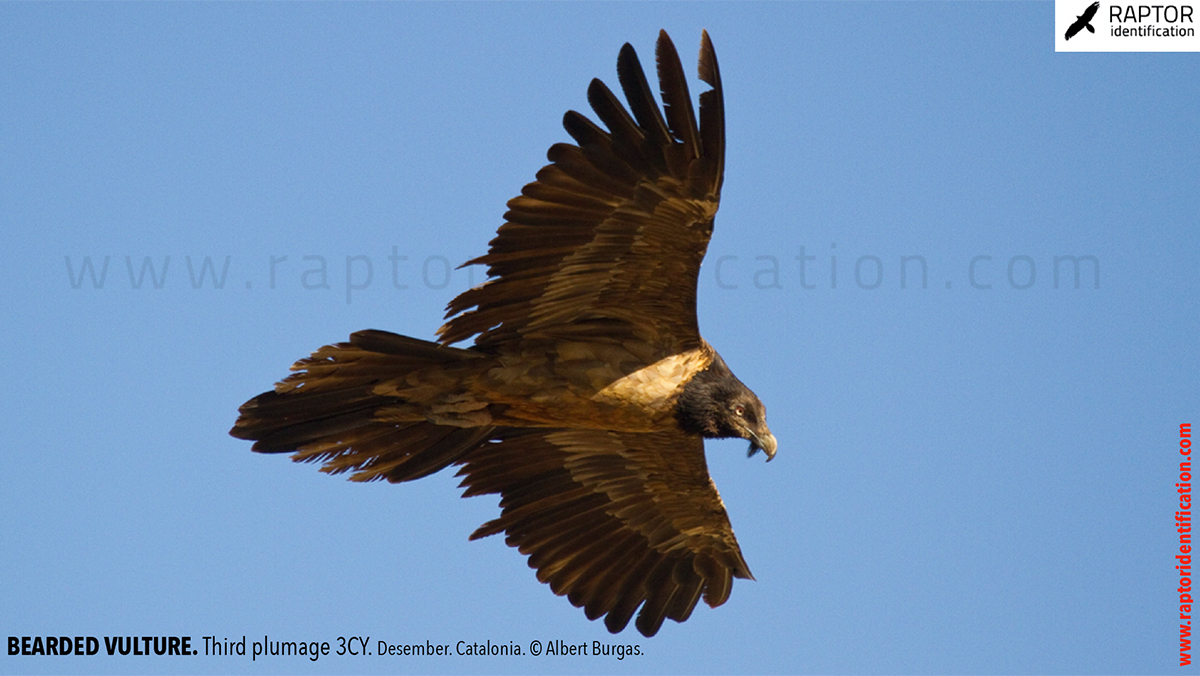
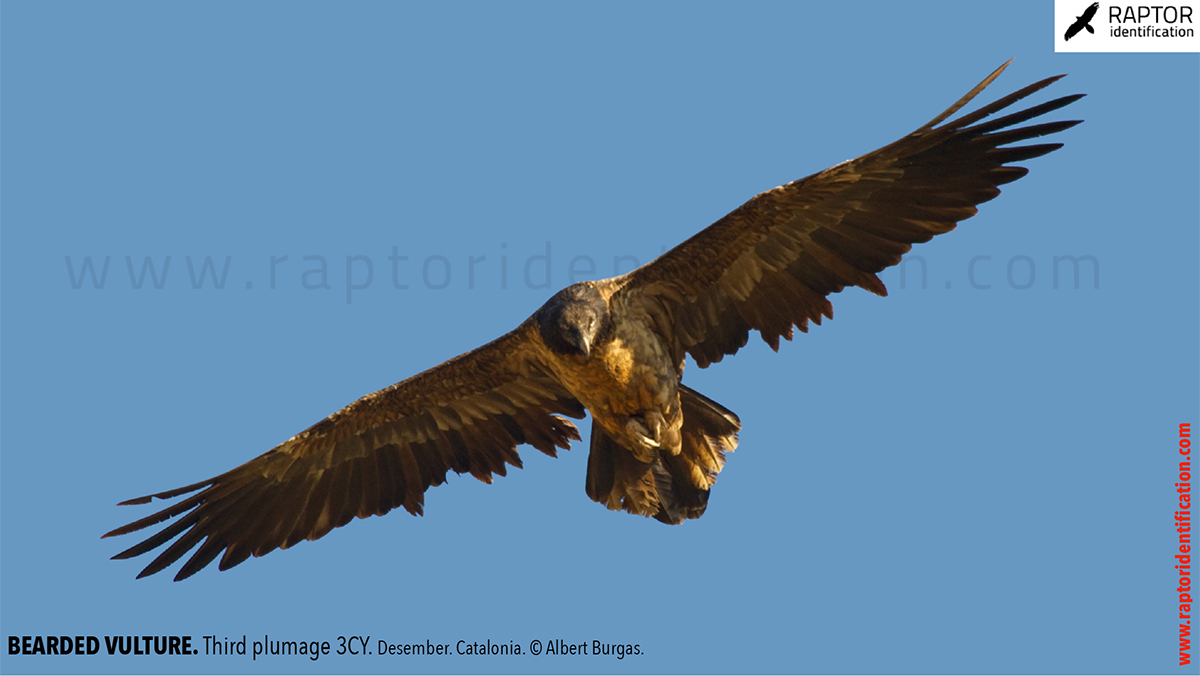
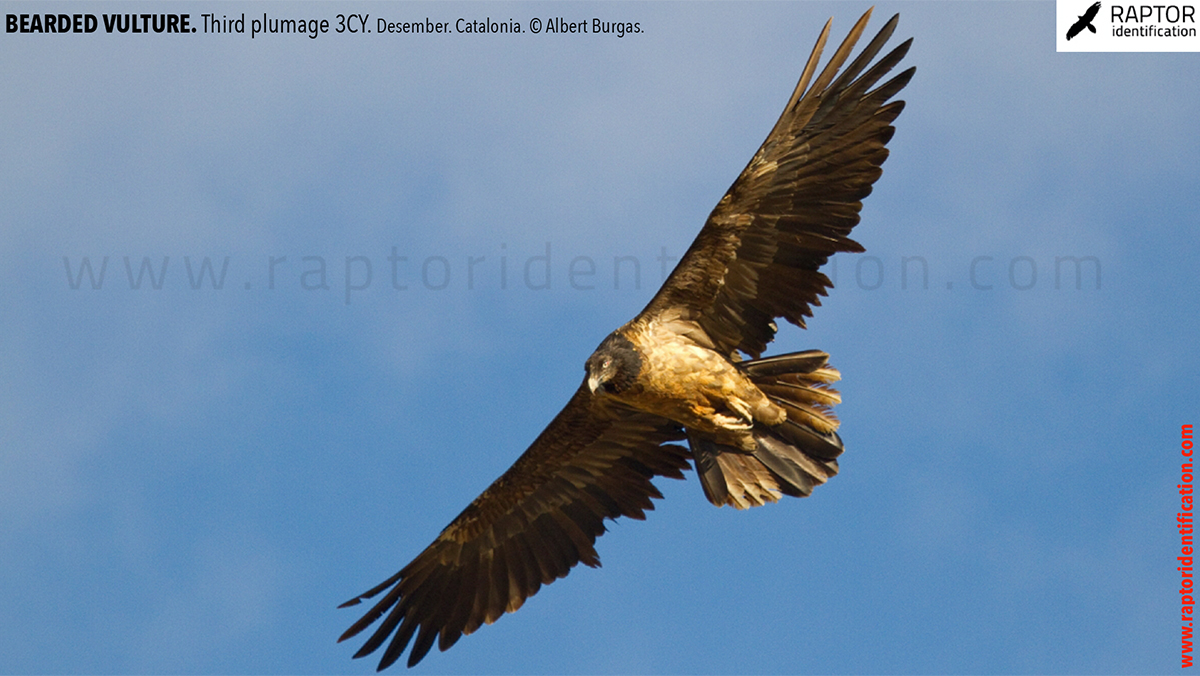
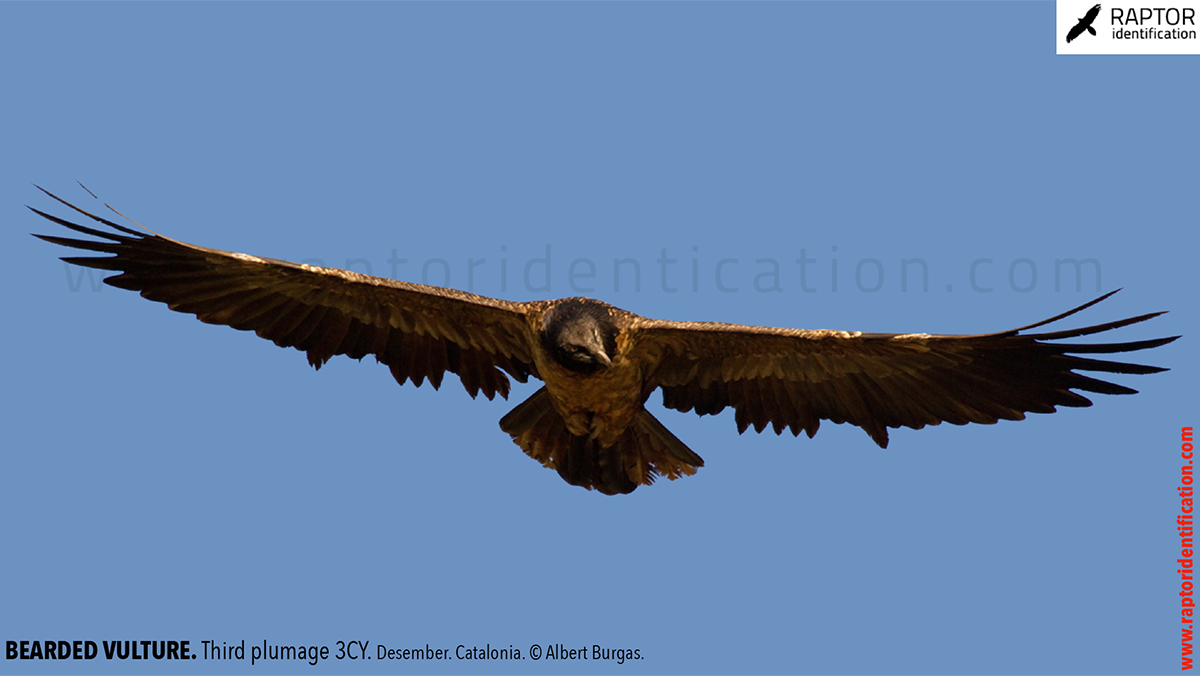
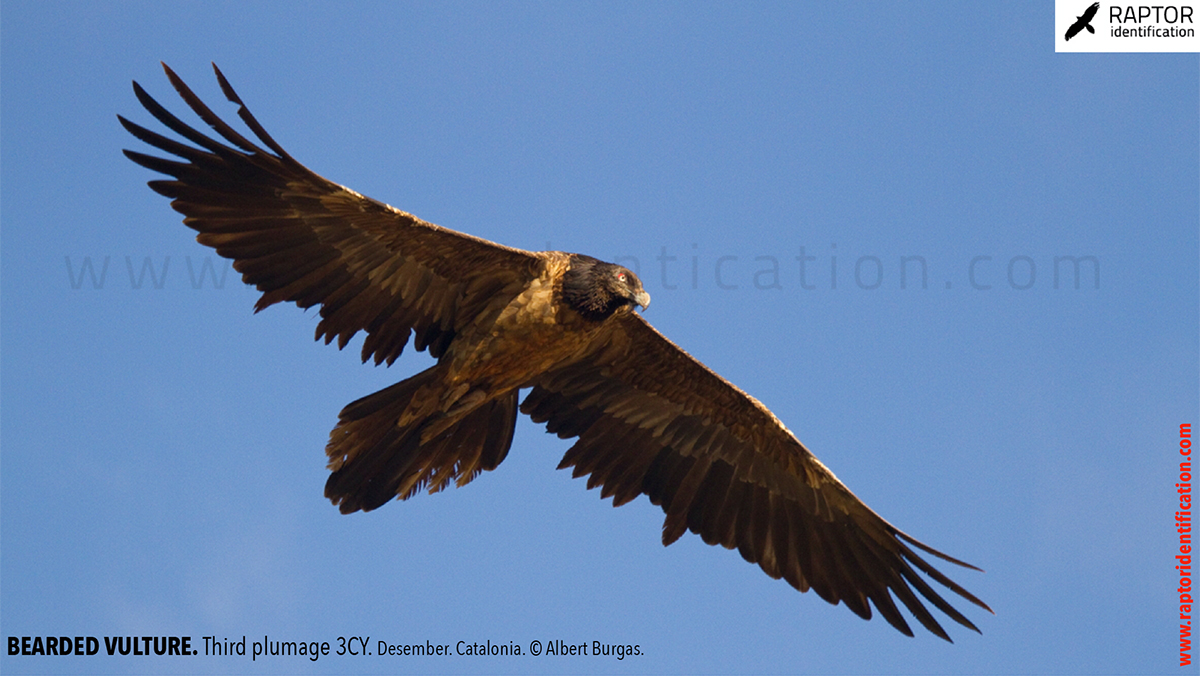
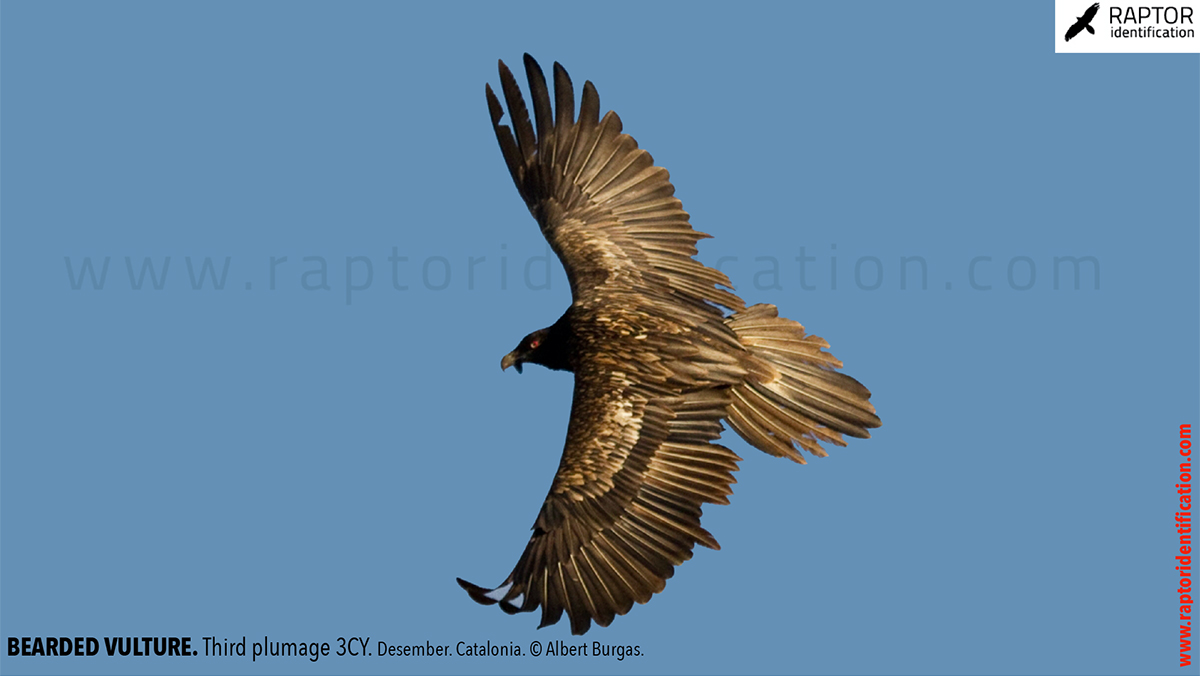
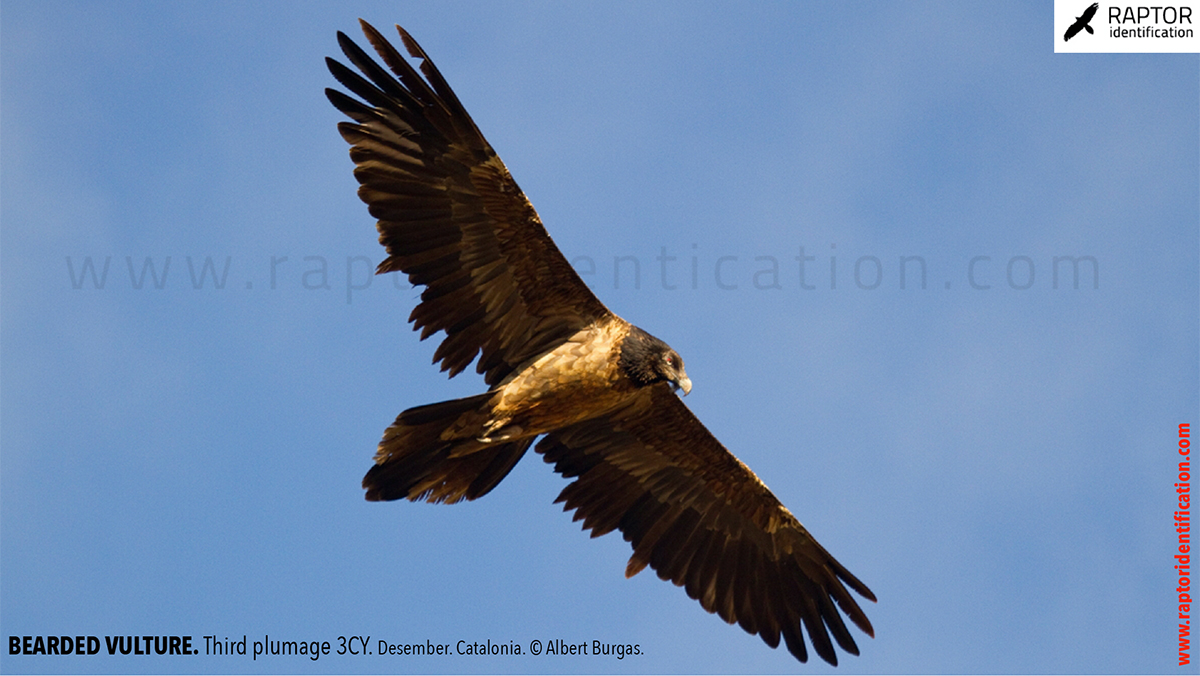
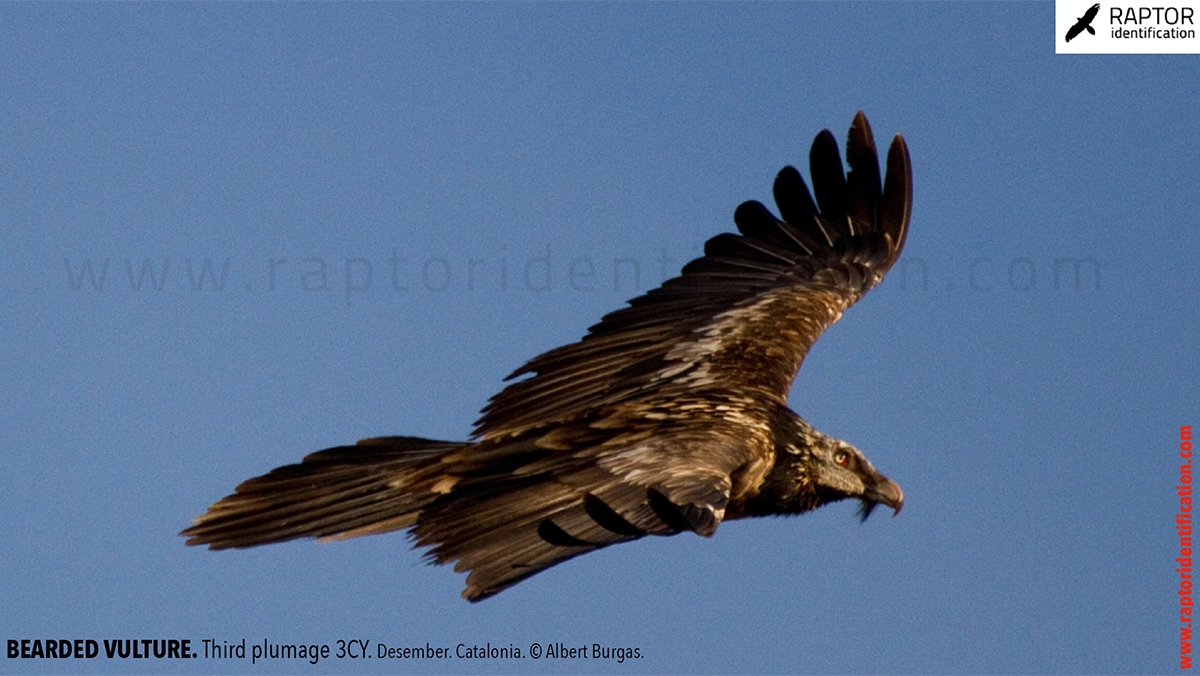
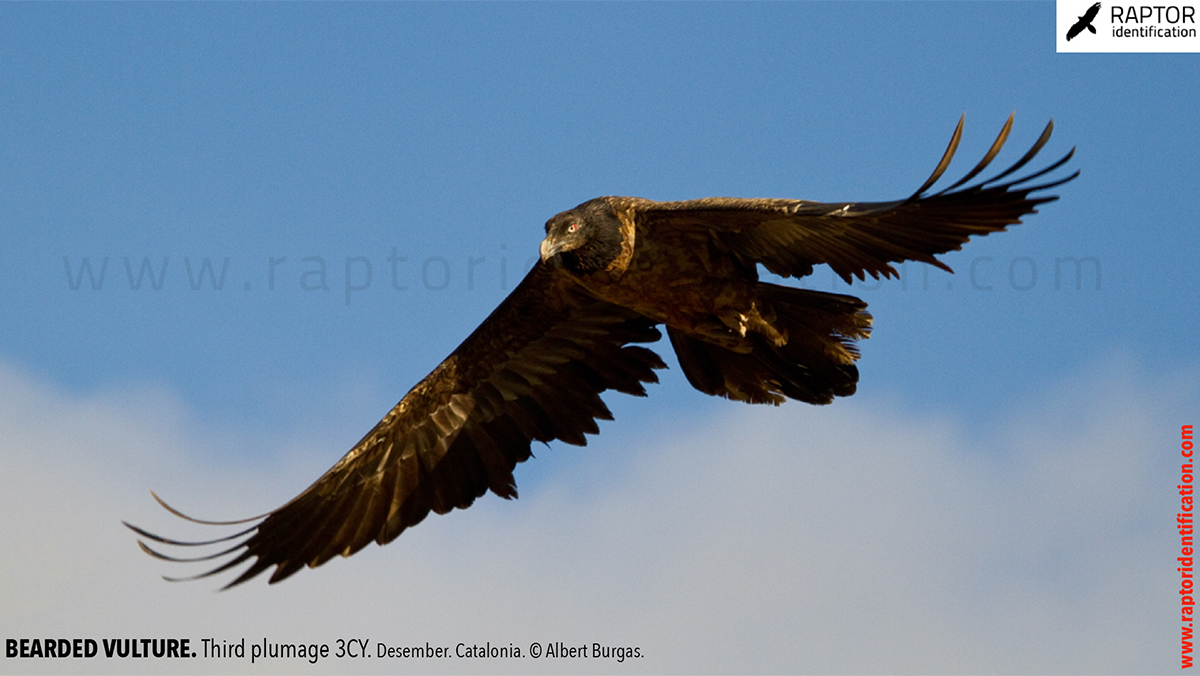
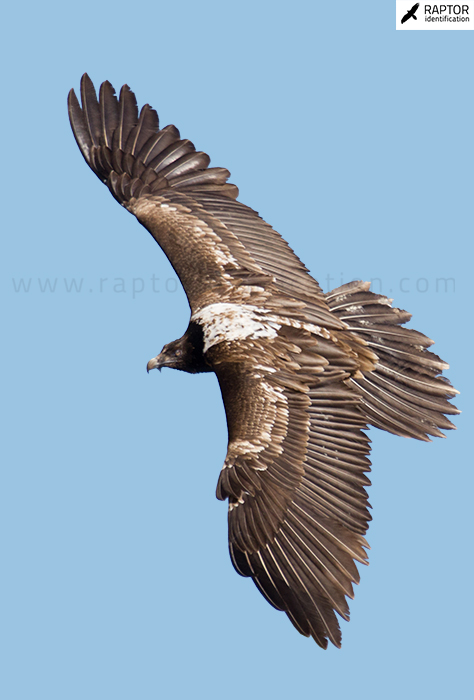
Third plumage: during the 3cy, all of the outermost primaries are moulted and the innermost primaries are replaced again. As a result, we can distinguish two waves of moult proceeding simultaneously. Also, a contrast between the new outermost and innermost primaries, and the old central ones.
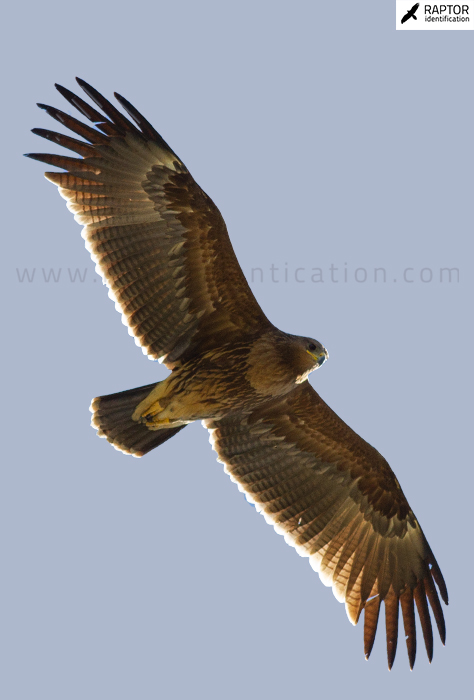
Adult plumage: adults moult during all year, except for when they migrate. Almost all primaries are replaced.
Hybrids: with Lesser Spotted Eagle in North-east Europe, from Eastern Poland to Western Russia, all the way across Belarus, central Ukraine, Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia, affecting up to 80% of cases in some countries.
Similar especies: Lesser Spotted Eagle.
Bibliography:
MACIOROWSKI, G. LONTKOWSKI, J. & MIZERA, T. 2014. The Spotted Eagle – Vanishing Bird of the Marshes. Unigraf. Poznán.